What Is A Refractor Telescope? How Is It Different From Other Telescopes
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and I may earn a small commission (at no extra cost to you) if you click through and make a purchase. Thanks in advance – I really appreciate it!
When a wave such as light passes from one medium to another at an angle it changes direction. This is called refraction. A lens is a piece of glass designed to bend the light that passes through it in such a way that an image may be produced.
Now you may wonder, how does all this work in a refractor telescope? What exactly is a refractor telescope?
Key Takeaways:
Refractor telescopes use a convex lens at one end of the optical tube which gathers the light coming from a distant object, such as a star, and bends it into a single point of focus. A second lens or the eyepiece at the other end of the optical tube then enlarges that focused image.
If you want to learn more about Refractor telescopes and how do they compare with Reflectors and Catadioptric telescopes, then read on!
Related: Best Refractor Telescope For Beginners; Reviews
How Do The Refractor Telescopes Work
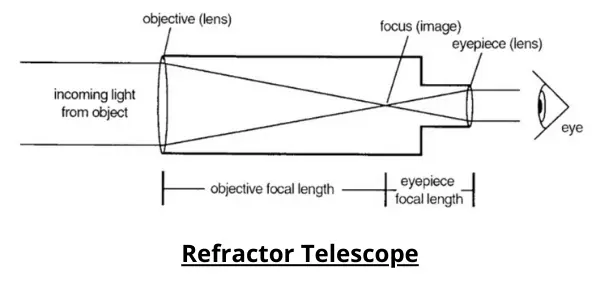
A simple refracting telescope consists of two lenses, the Objective and the eyepiece.
Basically, the objective lens produces an image of a distant object at its focus and the eyepiece lens magnifies this image.
As light passes through the lens at the front end of the optical tube, they are split into their respective colors or wavelengths.
They continue to travel through the optical tube and eventually meet at a focal point within the tube while parallel lightwaves fall onto a focal plane.
A second lens which is the eyepiece then enlarges that focused image for the retina of our eyes.
The eyepiece basically acts as a magnifying glass.
You could have an eyepiece directly in the path of the light, but if the eyepiece were at the end of the tube and you had the telescope pointed high in the sky you would have to be down on your knees to look through the eyepiece.
For this reason, the refractor telescopes usually have a diagonal in the light path that bends the light through a 90-degree angle to place the eyepiece at a more convenient position so that you don’t have to get into awkward positions to view the night sky.
The eyepiece is usually inserted into the diagonal. There are diagonals that use a 45-degree angle but these are better for daytime spotting scope use. For astronomy, you want a 90-degree “star diagonal”.
A refractor with diagonal presents an image that is correct up and down but reversed left and right.
For astronomy purposes, this left-right flip is of little importance as there is no left and right in space.
If you want to use your refractor for terrestrial viewing during the day, you can get a diagonal that has a prism to correct this left/right flip.
Related: Best Refractor Telescope; Reviews
Refractor Aperture Size
Refractors are typically sold with apertures no larger than 6 inches. A 6” refractor is a massive telescope and with its mount will easily exceed 100 pounds.
Larger sizes are even more unwieldy, and due to the prices of the special glass needed for the objective lens as well as the difficulty in manufacture, the prices skyrocket. As a result, you rarely ever see amateurs with larger refractors.
Related: Best Telescope For Beginners; Reviews
Chromatic Aberration
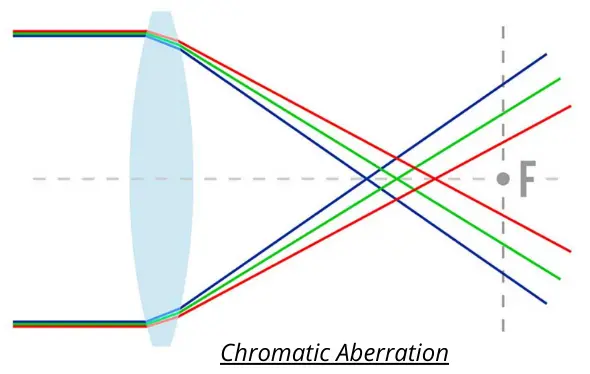
When the light enters the lens at the front end of the optical end, it splits into their respective wavelengths, but not all the wavelengths will be capable of meeting at the same focal point unless additional glass elements are used.
When this happens, an optical aberration called chromatic aberration is seen.
The glass lens elements in a refractor are unable to focus all the colors of light at the exact same position because the refractive index of glass varies with the wavelength of the light passing through it, resulting in color fringing.
Blue light is refracted more than, say, red light. This means that the different wavelengths have different focal lengths. The refractive index of blue light is greater than that of red light.
If one imagines the effect of this on the formation of an image of an object, then the blue light will be found at a different location than the red light.
This means that the image produced is blurred. It also means a difference in the magnification of different colors.
In plain language, this means that the different image distances for the respective colors cause different image sizes for them.
This means the production of annoying color fringes in the image.
Chromatic aberration is reduced to negligible levels either by making the telescope’s focal ratio longer (above f/10) in achromats or by adding special types of glass or extra lens elements to create ED doublets or apochromats.
The apochromats are heavier, expensive, and more optimized for photographic uses. Most refractors sold to beginners are achromats.
Related: Best Telescope Under $300; Reviews
Good Refractor Telescopes For Beginners
Celestron – AstroMaster 70AZ
- Powerful refractor telescope: The Celestron AstroMaster 70AZ is a powerful and user-friendly refractor telescope with fully coated glass optics, a sturdy yet lightweight frame, 2 eyepieces, a red dot finder scope, and an adjustable-height tripod.
- High-quality 70mm optics: Our Celestron telescope features a powerful, fully coated 70mm glass optic objective lens. Erect image optics allow you to observe celestial objects at night and terrestrial targets like wildlife and landscapes during the day.
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
With Celestron – Astromaster 70AZ you’ll be ready to observe the night sky in minutes thanks to the quick and easy no-tool setup. The 70AZ provides bright, clear images of the Moon, planets, star clusters, and more for great nighttime viewing.
Accessories include a 20mm and 10mm eyepiece, an erect image diagonal, and a Starpointer finderscope. The two eyepieces offer different magnifications for low and high-powered views.
The telescope makes it possible to view the moon, stars, planets, and nebulae, and on very clear nights, it can even allow a user to catch sight of the moons of Jupiter and the rings of Saturn.
Click here to check the price on Amazon.
Gskyer Telescope 70mm
- Quality Optics: 400mm(f/5.7) focal length and 70mm aperture, fully coated optics glass lens with high transmission coatings creates stunning images and protect your eyes. Perfect telescope for astronomers to explore stars and moon.
- Magnification: Come with two replaceable eyepieces and one 3x Barlow lens.3x Barlow lens trebles the magnifying power of each eyepiece. 5x24 finder scope with mounting bracket and cross-hair lines inside make locating objects easily.
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
The Gskyer is an entry-level telescope with the very basics. Even so, it performs better than many other comparable scopes in its budget range.
The Gskyer’s AZ70400 Telescope package is a 70 mm short focal length refractor mounted on a camera-type tripod. It includes a 45 degree diagonal, a carry case, finder scope, two eyepieces, and a 3X Barlow lens.
With a basic, fluid, altazimuth mount, this telescope is super easy to use. It won’t be long before you are casually cruising around the night sky looking for interesting things to view. This makes it perfect for children or young astronomers as well.
Click here to check the price on Amazon.
Celestron – 70mm Travel Scope
- Superior optics: The Celestron 70mm Travel Scope features high-quality, fully-coated glass optics, a potent 70mm objective lens, a lightweight frame, and a custom backpack to carry it all. Its quality is unmatched in its class and against competitors.
- Powerful eyepieces for up-close viewing: Our telescope for astronomy beginners is equipped with two high-quality eyepieces (20mm and 10mm) that provide low- and high-power views of celestial objects at night and terrestrial objects during the day.
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
The Celestron 70mm Travel Scope is an excellent choice of telescope for those seeking an easy-to-use, portable scope. The Travel Scope is a great choice for both beginners who are looking to start off their astronomical careers and for intermediate astronomers looking to refine their skills.
This Celestron’s best feature is its lightweight portability. It is well-suited for traveling astronomers who need to take their telescope on the go. The Travel Scope also comes pre-assembled and ready-to-use, so you can just grab it and go.
Click here to check the price on Amazon.
Orion 10034 GoScope II
- Grab-and-go day and night refractor telescope and lightweight aluminum tripod for young stargazers and families on the go
- Rugged, specially designed backpack holds the 70mm telescope, tripod and all accessories
- 400mm focal length telescope (f/5.7) excels at daytime birding use as well as viewing wildlife, scenery and casual nighttime observing of the Moon and bright planets
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
The Orion GoScope II 70mm Refractor Travel Telescope is perfect for beginners and kids as they can still enjoy sharp daytime terrestrial views and night sky observations while on the road, and save storage space in the car by bringing along this portable telescope and Moon Kit.
It’s a versatile 70mm-aperture refractor telescope designed to pack up and go whenever you hit the road, the trail, or even the air.
The GoScope II’s custom backpack and small stature make portable stargazing and daytime spotting a convenient reality, without compromising quality.
Click here to check the price on Amazon.
Types Of Refractor Telescopes
There are two main types of Refractor Telescopes:
- Achromatic Refractors – Entry-level and upwards with 2 lens elements
- Apochromatic Refractors – Premium, advanced and expert level refractor telescopes with 3 or more very high-quality lens elements with exotic mixes of materials.
Achromatic Refractor Telescopes are particularly good for observing bright objects such as the moon, planets and resolving things like double stars, but many astronomers who image deep-sky and other objects use very high-quality apochromatic refractors, due to their superior optics.
Advantages Of Refractor Telescopes
- Refracting telescopes are easy to use and require minimum maintenance.
- They are usually small and compact.
- Refracting telescope is a good choice for kids.
- Refractors with complex lens designs are the number one choice for astrophotography.
- Since refractors have a closed tube design, the change in temperature doesn’t affect the stargazing experience.
- Refractors have superior resolving power per inch of aperture.
- Superior performance in inferior conditions – image steadier
- There are no reflections or interruptions of the light path
- Refractors’ long focal ratios can mean the use of longer focus and simpler eyepieces.
Disadvantages Of Refractor Telescopes
- Refractors suffer from an effect called chromatic aberration that produces a rainbow of colors around the image. Because of the wave nature of light, the longer wavelength light (redder colors) is bent less than the shorter wavelength light (bluer colors) as it passes through the lens. It can be corrected using achromatic and apochromatic (modified) lenses.
- Refractor telescopes come in very small aperture sizes as manufacturing a refractor with a large aperture is expensive.
- Good quality refractors with high-quality lenses called Apochromatic refractors are quite expensive.
- Since refractors come in smaller aperture sizes, they cannot gather enough light to observe deep-sky objects such as galaxies and nebulae.
Refractor Telescope Vs Reflector Telescope
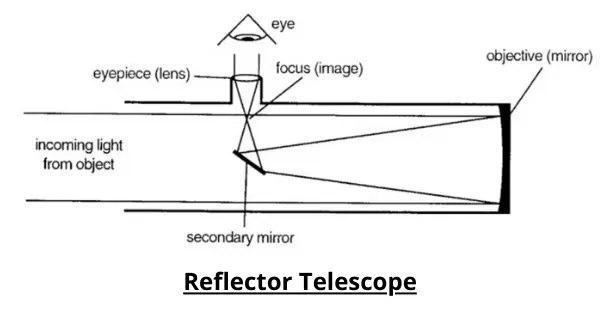
Where refractors use lenses to produce an image, the reflector telescopes use mirrors and a lens as the eyepiece.
It uses a concave, parabolic mirror to focus light, with a super-precise angled flat mirror deflecting the image outside the tube at a 90-degree angle to be viewed. The telescope’s focuser holds the eyepiece.
The reflector design produces an image that is rotated 180 degrees, or upside down (though not flipped left-right).
This is not a big issue for astronomical purposes, as there is no up or down in space. However, this does render this type of scope impractical for terrestrial observations.
Advantages Of Reflector Telescopes
- They are less expensive as it is cheaper to manufacture quality mirrors than lenses, especially as they get large.
- Reflectors are free of any chromatic aberration as mirrors also provide light that remains true to color. There is no splitting of the light into its color components as you get with the refractors.
- Reflectors are available in larger aperture sizes.
- Since reflectors come in larger aperture sizes, they are perfect for viewing deep-sky objects.
Disadvantages Of Reflector Telescopes
- They are difficult to maintain because of their open tube design and mirrors.
- Reflectors require regular collimation.
- They are heavy and bulkier than the same aperture size refractor.
- Because of the open tube design, the sudden temperature change can affect the image quality.
Refractor Telescope Vs Catadioptric Telescope
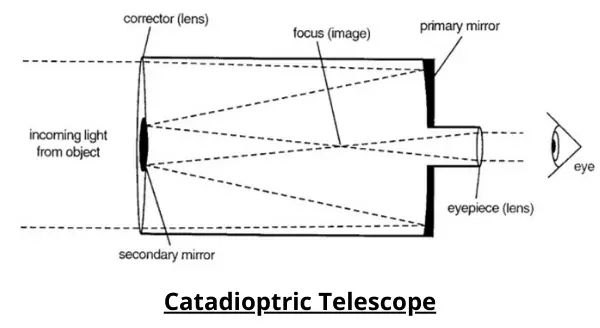
A catadioptric telescope is an optical system that is optimized for producing images of objects at an infinite distance, and which incorporates both refractive type optics (lenses) and reflective optics (mirrors).
The use of both mirror and lens optics produces certain advantages in performance as well as in the manufacturing process.
The term “catadioptric” results from two separate words: “catoptric” referring to an optical system that uses curved mirrors, and “dioptric” referring to one which uses lenses.
The four catadioptric telescope designs most commonly used by amateur astronomers are:
- Schmidt-Cassegrain
- Maksutov-Cassegrain
- Schmidt-Astrograph
- Schmidt-Newtonian
Advantages Of Catadioptric Telescopes
- Catadioptric Telescopes operate with a folded-path optical system, unlike refractors and Newtonian reflecting telescopes that use a linear optical path. This allows the telescope to be shorter than the size implied by its focal length.
- These telescopes and telescopic mounts are designed to be compact and weigh a lot less compared to telescopes of other designs having the same configuration.
- Catadioptric Telescopic designs have increased portability and are easy to transport. This is because they have a reduced mechanical size and weight.
- These telescopes use mirrors that have purely spherical figures and refractive elements that can be conveniently (generally termed as corrector lenses). Using such elements reduces the overall manufacturing costs of the telescope.
Disadvantages Of Catadioptric Telescopes
- Catadioptric telescopes become heavier rather quickly as they increase in aperture.
- They may require more frequent optical alignment when compared to refractors.
- A catadioptric telescope’s moving parts are more complex than those found in refractors.
Written by:

Kavya Joshi
My love affair with space began in a field in India at the age of 7, when I looked up at the Milky Way for the first time. Ever since, I have been attempting to cram in every fact about the Universe, I can find into my head.
ABOUT US
We are a team of active amateur astronomers, here to help you with all your astronomy and science related needs – this is anything, from reviewing the latest telescopes to be released to talking about gravity and neurons. The Big Bang Optics was started because of our love for astronomy and to help others like us find the best telescope and accessories.
LEGAL DISCLAIMER
The Big Bang Optics is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. The Big Bang Optics also participates in affiliate programs with Clickbank and other sites. The Big Bang Optics is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.








